9017. Binary search – 1
A sorted array
of n integers is given. You need to answer q queries:
how many times a given number x appears in the array.
Input. The first line
contains two numbers n and q (n, q ≤ 106). The second line contains n
integers sorted in increasing order. Each of the following q lines
contains a single value x. All numbers in the array do not exceed 109 in
absolute value.
Output. For each value
of x, print the number of times it occurs in the array in a
separate line.
|
Sample
input 1 |
Sample
output 1 |
|
6 3 2 4 4 8 11 14 10 4 2 |
0 2 1 |
|
|
|
|
Sample
input 2 |
Sample
output 2 |
|
8 4 -8 -8 -1 1 3 4 6 8 4 10 -4 -8 |
1 0 0 2 |
SOLUTION
binary search
Algorithm analysis
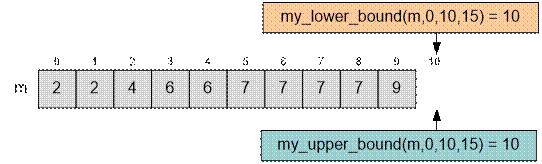
The number of occurrences of the number x
in the sorted array is equal to upper_bound(m,
m + n, x) – lower_bound(m, m + n, x). These functions can be
taken from the STL template library or implemented manually
(for example, in Java).
Let all n elements of the array m be located in cells from 0 to n – 1. In this case, the lower_bound and upper_bound functions can return
values in the range from 0 to n, so binary search should be performed
within these bounds.
Algorithm implementation
Declare an array.
#define MAX 1000000
int m[MAX];
Read the input data.
scanf("%d %d", &n,
&q);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d",
&m[i]);
Process
q queries sequentially. For each
query, read the value x and print the number of its occurrences in the
array m.
for (i = 0; i < q; i++)
{
scanf("%d",
&x);
res =
upper_bound(m, m + n, x) - lower_bound(m, m + n, x);
printf("%d\n",
res);
}
Algorithm implementation – own functions lower_bound, upper_bound
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX 1000000
int i, n, q, x, res;
int m[MAX];
int my_lower_bound(int *m, int start, int end, int x)
{
while (start < end)
{
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (x <= m[mid])
end = mid;
else
start = mid + 1;
}
return start;
}
int my_upper_bound(int *m, int start, int end, int x)
{
while (start < end)
{
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (x >= m[mid])
start = mid + 1;
else
end = mid;
}
return start;
}
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d %d", &n,
&q);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &m[i]);
for (i = 0; i < q; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &x);
res =
my_upper_bound(m, 0, n, x) – my_lower_bound(m, 0, n, x);
printf("%d\n", res);
}
return 0;
}
Java implementation
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main
{
static int my_lower_bound(int m[], int start, int end, int x)
{
while (start < end)
{
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (x <= m[mid])
end = mid;
else
start = mid + 1;
}
return start;
}
static int my_upper_bound(int m[], int start, int end, int x)
{
while (start < end)
{
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (x >= m[mid])
start = mid + 1;
else
end = mid;
}
return start;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
FastScanner con =
new FastScanner(new
InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n = con.nextInt();
int q = con.nextInt();
int m[] = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
m[i] = con.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i < q; i++)
{
int x = con.nextInt();
int res = my_upper_bound(m,0,n,x) - my_lower_bound(m,0,n,x);
System.out.println(res);
}
}
}
class FastScanner
{
private BufferedReader br;
private StringTokenizer st;
public
FastScanner(InputStreamReader reader)
{
br = new BufferedReader(reader);
}
public String next()
{
while (st == null || !st.hasMoreTokens())
{
try
{
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
public int nextInt()
{
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public double nextDouble()
{
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
public void close() throws Exception
{
br.close();
}
}
Python implementation
import bisect
Read the input data.
n, q = map(int, input().split())
lst = list(map(int, input().split()))
Process
q queries sequentially. For each
query, read the value x and print the number of its occurrences in the list
lst.
for _ in range(q):
x = int(input())
res = bisect.bisect_right(lst, x) -
bisect.bisect_left(lst, x)
print(res)